
OpticsPOD
What's New
Rays & Shadows
Water Droplets
Rainbows
Not a rainbow!
Primary Bow
Secondary Bow
Formation
A's Dark Band
Other Orders
Supernumeraries
Red Bows
Rainbow Wheel
Dew Bow
Sea Spray Bow
Glass Bead Bows
Reflection Bows
Twinned Bows
Cloud Bows
Moon Bows
Image Gallery
Simulators
Ice Halos
High Atmosphere
Links & Resources
Search - Index
123456789012345678
| Secondary Bow Formation |
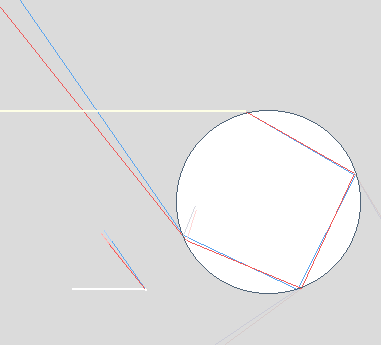 |

 |
| Light
emerging after two internal reflections forms the secondary
bow. Light reflected more than twice goes into higher
order bows. |
Two
internal reflections. |
|||
| Mouse
over the slider to see the ray paths. Compare them with those of the
primary bow, shown faintly here and more completely in the primary
ray diagram. |
Many different ray paths | |||
| Secondary
bow rays* are deviated**
through more than 180º. There is a minimum deviation of
about 231º corresponding to the inner edge of the secondary
bow. Its radius is therefore 231 - 180 = 51º. Rays cluster around
the minimum deviation condition to form the brightest part of the
bow. |
Minimum deviation angle | |||
| The
minimum
deviation rays enter much closer to the drop's edge than the corresponding
rays of the primary bow. |
Closer to the drop edge | |||
| Why
are the secondary colours reversed? Red light is refracted least and
so its rays suffer the smallest deviation. But the total deviation
is more than 180º and the least deviated rays appear at the inside
of the bow. |
Colour reversal | |||
| No
light from secondary rays appears at less than 51º from
the center and no light from the primary appears more than
than 42º. The sky between is dark (but not quite, see the
5th order bow). This is Alexanders
dark band. |
Inside the bow is dark | |||
| * | Ray
paths are a good approximation to how light behaves when the raindrops
are several millimetres across. Smaller drops require a treatment
which takes account of the wave nature of light. |
Don't take ray paths too seriously | ||
| ** | Deviations
are traditionally measured from the direction of the incoming sunlight. |
Deviation angles | ||
| *** | The
ray paths are accurately computed for wavelengths of 400 and 750 nm
passing through a water drop at 0 Celsius. |
Calculation | ||