OPOD
What's New
Rays & Shadows
Crepuscular rays
Anti-crepuscular
Cloud shadows
Mountain Shadow
Earth's Shadow Blue Sky
Sunsets
Volcanic ash
Flattened Suns
Sunrise eclipse
Infrared sunset
More Images
Sunset Mirages
Green Flash
Moonrise/set
Opposition effect
Water Droplets
Rainbows
Ice Halos
High Atmosphere
Links & Resources
Search - Index
123456789012345678

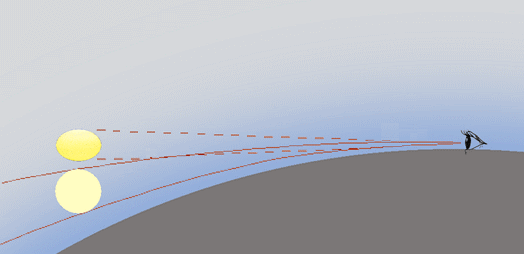
| Flattened Suns |
|
Density gradients in the atmosphere cause it to act like a lens.
Rays bend towards the higher density. Higher density
is associated with higher pressure and lower temperature so a useful
guideline for atmospheric refraction or mirages is that rays bend
towards higher pressure and to cooler air. Incoming rays from the Sun curve downwards so that it appears higher in the sky than it really is. The Moon and stars and the whole sky are similarly raised and astronomical observations are routinely corrected for "atmospheric refraction". The effect is small except near to the horizon when the rays are literally bent a little around the curve of the Earth. When the lower limb of the Sun just touches the sea horizon the whole Sun has actually already set. Objects closer to the horizon are raised upwards most and the lower limb of the Sun is raised more than the top making it appear oval. The blue and green images of the sun are raised more than the red. However this effect is very small and is not the cause of the green flash. The flattening is up to about 20% for a normal atmospheric temperature profile and an observer close to sea level. It varies with atmospheric conditions especially when there are abnormal temperature gradients. From high aircraft or space the flattening is much greater.
|